- Current software
- All software
Structural Bioinformatics
 The BetaWrap program detects the right-handed parallel
beta-helix super-secondary structural motif in primary
amino acid sequences by using beta-strand interactions
learned from non-beta-helix structures.
The BetaWrap program detects the right-handed parallel
beta-helix super-secondary structural motif in primary
amino acid sequences by using beta-strand interactions
learned from non-beta-helix structures.
 Wrap-and-pack detects beta-trefoils in protein sequences
by using both pairwise beta-strand interactions and 3-D
energetic packing information
Wrap-and-pack detects beta-trefoils in protein sequences
by using both pairwise beta-strand interactions and 3-D
energetic packing information
 The BetaWrapPro program predicts right-handed beta-helices
and beta-trefoils by using both sequence profiles and
pairwise beta-strand interactions, and returns coordinates
for the structure.
The BetaWrapPro program predicts right-handed beta-helices
and beta-trefoils by using both sequence profiles and
pairwise beta-strand interactions, and returns coordinates
for the structure.
 The MSARi program indentifies conserved RNA secondary
structure in non-coding RNA genes and mRNAs by searching
multiple sequence alignments of a large set of candidate
catalogs for correlated arrangements of reverse-complementary
regions
The MSARi program indentifies conserved RNA secondary
structure in non-coding RNA genes and mRNAs by searching
multiple sequence alignments of a large set of candidate
catalogs for correlated arrangements of reverse-complementary
regions
 The Paircoil2 program predicts coiled-coil domains in
protein sequences by using pairwise residue correlations
obtained from a coiled-coil database. The original Paircoil
program is still available for use.
The Paircoil2 program predicts coiled-coil domains in
protein sequences by using pairwise residue correlations
obtained from a coiled-coil database. The original Paircoil
program is still available for use.
The MultiCoil program predicts the location of coiled-coil
regions in amino acid sequences and classifies the predictions
as dimeric or trimeric. An updated version, Multicoil2, will
soon be available.
The LearnCoil Histidase Kinase program uses an iterative
learning algorithm to detect possible coiled-coil domains
in histidase kinase receptors.
The LearnCoil-VMF program uses an iterative learning
algorithm to detect coiled-coil-like regions in viral
membrane-fusion proteins.
 The Trilogy program discovers novel sequence-structure patterns
in proteins by exhaustively searching through three-residue motifs
using both sequence and structure information.
The Trilogy program discovers novel sequence-structure patterns
in proteins by exhaustively searching through three-residue motifs
using both sequence and structure information.
 The ChainTweak program efficiently samples from the neighborhood
of a given base configuration by iteratively modifying a conformation
using a dihedral angle representation.
The ChainTweak program efficiently samples from the neighborhood
of a given base configuration by iteratively modifying a conformation
using a dihedral angle representation.
 The TreePack program uses a tree-decomposition based algorithm to
solve the side-chain packing problem more efficiently. This algorithm
is more efficient than SCWRL 3.0 while maintaining the same level of
accuracy.
The TreePack program uses a tree-decomposition based algorithm to
solve the side-chain packing problem more efficiently. This algorithm
is more efficient than SCWRL 3.0 while maintaining the same level of
accuracy.
 PartiFold: Ensemble prediction of transmembrane protein structures.
Using statistical mechanics principles, partiFold computes residue
contact probabilities and sample super-secondary structures from
sequence only.
PartiFold: Ensemble prediction of transmembrane protein structures.
Using statistical mechanics principles, partiFold computes residue
contact probabilities and sample super-secondary structures from
sequence only.
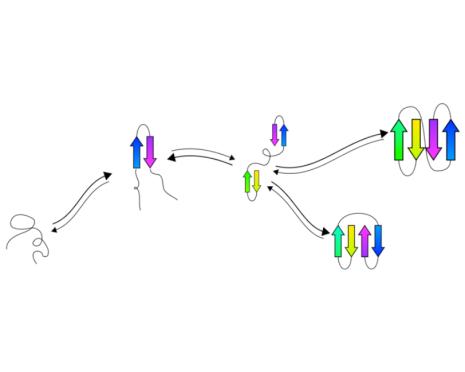 tFolder: Prediction of beta sheet folding pathways.
Predict a coarse grained representation of the folding pathway of
beta sheet proteins in a couple of minutes.
tFolder: Prediction of beta sheet folding pathways.
Predict a coarse grained representation of the folding pathway of
beta sheet proteins in a couple of minutes.
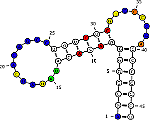 RNAmutants: Algorithms for exploring the RNA mutational landscape.
Predict the effect of mutations on structures and reciprocally the
influence of structures on mutations. A tool for molecular evolution
studies and RNA design.
RNAmutants: Algorithms for exploring the RNA mutational landscape.
Predict the effect of mutations on structures and reciprocally the
influence of structures on mutations. A tool for molecular evolution
studies and RNA design.
 AmyloidMutants
is a statistical mechanics approach for de novo prediction and analysis of wild-type and mutant amyloid structures. Based on the premise of protein mutational landscapes, AmyloidMutants energetically quantifies the effects of sequence mutation on fibril conformation and stability.
AmyloidMutants
is a statistical mechanics approach for de novo prediction and analysis of wild-type and mutant amyloid structures. Based on the premise of protein mutational landscapes, AmyloidMutants energetically quantifies the effects of sequence mutation on fibril conformation and stability.
Genomics
 GLASS aligns large orthologous genomic regions using an
iterative global alignment system. Rosetta identifies
genes based on conservation of exonic features in sequences
aligned by GLASS.
GLASS aligns large orthologous genomic regions using an
iterative global alignment system. Rosetta identifies
genes based on conservation of exonic features in sequences
aligned by GLASS.
RNAiCut -
Automated Detection of Significant Genes from Functional Genomic Screens.
 MinoTar
- Predict microRNA Targets in Coding Sequence.
MinoTar
- Predict microRNA Targets in Coding Sequence.
Systems Biology
 The Struct2Net program predicts protein-protein interactions
(PPI) by integrating structure-based information with other
functional annotations, e.g. GO, co-expression and co-localization
etc. The structure-based protein interaction prediction is
conducted using a protein threading server RAPTOR plus logistic
regression.
The Struct2Net program predicts protein-protein interactions
(PPI) by integrating structure-based information with other
functional annotations, e.g. GO, co-expression and co-localization
etc. The structure-based protein interaction prediction is
conducted using a protein threading server RAPTOR plus logistic
regression.
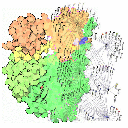 IsoRank is an algorithm for global alignment of multiple
protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. The intuition
is that a protein in one PPI network is a good match for
a protein in another network if the former's neighbors are
good matches for the latter's neighbors.
IsoRank is an algorithm for global alignment of multiple
protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks. The intuition
is that a protein in one PPI network is a good match for
a protein in another network if the former's neighbors are
good matches for the latter's neighbors.
Other
 t-sample is an online algorithm for time-series experiments
that allows an experimenter to determine which biological
samples should be hybridized to arrays to recover expression
profiles within a given error bound.
t-sample is an online algorithm for time-series experiments
that allows an experimenter to determine which biological
samples should be hybridized to arrays to recover expression
profiles within a given error bound.