 Intent
Intent Intent
IntentWithout violating encapsulation, capture and externalize an object's internal state so that the object can be restored to this state later.
 Also Known As
Also Known AsToken
 Motivation
MotivationSometimes it's necessary to record the internal state of an object. This is required when implementing checkpoints and undo mechanisms that let users back out of tentative operations or recover from errors. You must save state information somewhere so that you can restore objects to their previous states. But objects normally encapsulate some or all of their state, making it inaccessible to other objects and impossible to save externally. Exposing this state would violate encapsulation, which can compromise the application's reliability and extensibility.
Consider for example a graphical editor that supports connectivity between objects. A user can connect two rectangles with a line, and the rectangles stay connected when the user moves either of them. The editor ensures that the line stretches to maintain the connection.
A well-known way to maintain connectivity relationships between objects is with a constraint-solving system. We can encapsulate this functionality in a ConstraintSolver object. ConstraintSolver records connections as they are made and generates mathematical equations that describe them. It solves these equations whenever the user makes a connection or otherwise modifies the diagram. ConstraintSolver uses the results of its calculations to rearrange the graphics so that they maintain the proper connections.
Supporting undo in this application isn't as easy as it may seem. An obvious way to undo a move operation is to store the original distance moved and move the object back an equivalent distance. However, this does not guarantee all objects will appear where they did before. Suppose there is some slack in the connection. In that case, simply moving the rectangle back to its original location won't necessarily achieve the desired effect.
In general, the ConstraintSolver's public interface might be insufficient to allow precise reversal of its effects on other objects. The undo mechanism must work more closely with ConstraintSolver to reestablish previous state, but we should also avoid exposing the ConstraintSolver's internals to the undo mechanism.
We can solve this problem with the Memento pattern. A memento is an object that stores a snapshot of the internal state of another object—the memento's originator. The undo mechanism will request a memento from the originator when it needs to checkpoint the originator's state. The originator initializes the memento with information that characterizes its current state. Only the originator can store and retrieve information from the memento—the memento is "opaque" to other objects.
In the graphical editor example just discussed, the ConstraintSolver can act as an originator. The following sequence of events characterizes the undo process:
This arrangement lets the ConstraintSolver entrust other objects with the information it needs to revert to a previous state without exposing its internal structure and representations.
 Applicability
ApplicabilityUse the Memento pattern when
 Structure
Structure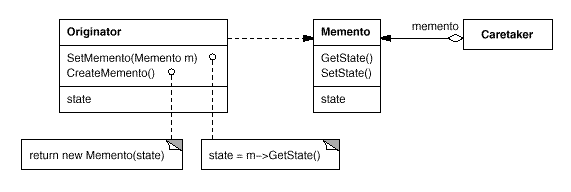
 Participants
Participants Collaborations
Collaborations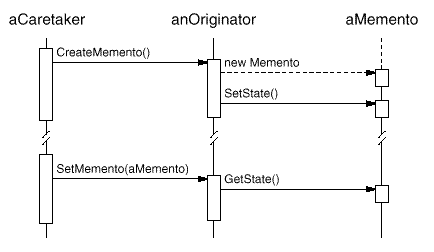
Sometimes the caretaker won't pass the memento back to the originator, because the originator might never need to revert to an earlier state.
 Consequences
ConsequencesThe Memento pattern has several consequences:
 Implementation
ImplementationHere are two issues to consider when implementing the Memento pattern:
class State;
class Originator {
public:
Memento* CreateMemento();
void SetMemento(const Memento*);
// ...
private:
State* _state; // internal data structures
// ...
};
class Memento {
public:
// narrow public interface
virtual ~Memento();
private:
// private members accessible only to Originator
friend class Originator;
Memento();
void SetState(State*);
State* GetState();
// ...
private:
State* _state;
// ...
};
For example, undoable commands in a history list can use mementos to ensure that commands are restored to their exact state when they're undone (see Command (233)). The history list defines a specific order in which commands can be undone and redone. That means mementos can store just the incremental change that a command makes rather than the full state of every object they affect. In the Motivation example given earlier, the constraint solver can store only those internal structures that change to keep the line connecting the rectangles, as opposed to storing the absolute positions of these objects.
 Sample Code
Sample CodeThe C++ code given here illustrates the ConstraintSolver example
discussed earlier. We
use MoveCommand objects (see Command (233)) to (un)do
the translation of a graphical object from one position to another.
The graphical editor calls the command's Execute operation
to move a graphical object and Unexecute to undo the move.
The command stores its target, the distance moved, and an instance of
ConstraintSolverMemento, a memento containing state from the
constraint solver.
class Graphic;
// base class for graphical objects in the graphical editor
class MoveCommand {
public:
MoveCommand(Graphic* target, const Point& delta);
void Execute();
void Unexecute();
private:
ConstraintSolverMemento* _state;
Point _delta;
Graphic* _target;
};
The connection constraints are established by the class
ConstraintSolver. Its key member function is
Solve, which solves the constraints registered with
the AddConstraint operation. To support undo,
ConstraintSolver's state can be externalized with
CreateMemento into a ConstraintSolverMemento
instance. The constraint solver can be returned to a previous
state by calling SetMemento. ConstraintSolver
is a Singleton (127).
class ConstraintSolver {
public:
static ConstraintSolver* Instance();
void Solve();
void AddConstraint(
Graphic* startConnection, Graphic* endConnection
);
void RemoveConstraint(
Graphic* startConnection, Graphic* endConnection
);
ConstraintSolverMemento* CreateMemento();
void SetMemento(ConstraintSolverMemento*);
private:
// nontrivial state and operations for enforcing
// connectivity semantics
};
class ConstraintSolverMemento {
public:
virtual ~ConstraintSolverMemento();
private:
friend class ConstraintSolver;
ConstraintSolverMemento();
// private constraint solver state
};
Given these interfaces, we can implement MoveCommand members
Execute and Unexecute as follows:
void MoveCommand::Execute () {
ConstraintSolver* solver = ConstraintSolver::Instance();
_state = solver->CreateMemento(); // create a memento
_target->Move(_delta);
solver->Solve();
}
void MoveCommand::Unexecute () {
ConstraintSolver* solver = ConstraintSolver::Instance();
_target->Move(-_delta);
solver->SetMemento(_state); // restore solver state
solver->Solve();
}
Execute acquires a ConstraintSolverMemento memento
before it moves the graphic. Unexecute moves the graphic
back, sets the constraint solver's state to the previous state, and
finally tells the constraint solver to solve the constraints.
 Known Uses
Known UsesThe preceding sample code is based on Unidraw's support for connectivity through its CSolver class [VL90].
Collections in Dylan [App92] provide an iteration interface that reflects the Memento pattern. Dylan's collections have the notion of a "state" object, which is a memento that represents the state of the iteration. Each collection can represent the current state of the iteration in any way it chooses; the representation is completely hidden from clients. The Dylan iteration approach might be translated to C++ as follows:
template <class Item>
class Collection {
public:
Collection();
IterationState* CreateInitialState();
void Next(IterationState*);
bool IsDone(const IterationState*) const;
Item CurrentItem(const IterationState*) const;
IterationState* Copy(const IterationState*) const;
void Append(const Item&);
void Remove(const Item&);
// ...
};
CreateInitialState returns an initialized
IterationState object for the collection. Next advances
the state object to the next position in the iteration; it effectively
increments the iteration index. IsDone returns
true if Next has advanced beyond the last element
in the collection. CurrentItem dereferences the state
object and returns the element in the collection to which it refers.
Copy returns a copy of the given state object. This is
useful for marking a point in an iteration.
Given a class ItemType, we can iterate over a collection of
its instances as follows7:
class ItemType {
public:
void Process();
// ...
};
Collection<ItemType*> aCollection;
IterationState* state;
state = aCollection.CreateInitialState();
while (!aCollection.IsDone(state)) {
aCollection.CurrentItem(state)->Process();
aCollection.Next(state);
}
delete state;
The memento-based iteration interface has two interesting benefits:
Collection is a friend of the
IteratorState.The QOCA constraint-solving toolkit stores incremental information in mementos [HHMV92]. Clients can obtain a memento that characterizes the current solution to a system of constraints. The memento contains only those constraint variables that have changed since the last solution. Usually only a small subset of the solver's variables changes for each new solution. This subset is enough to return the solver to the preceding solution; reverting to earlier solutions requires restoring mementos from the intervening solutions. Hence you can't set mementos in any order; QOCA relies on a history mechanism to revert to earlier solutions.
 Related Patterns
Related PatternsCommand (233): Commands can use mementos to maintain state for undoable operations.
Iterator (257): Mementos can be used for iteration as described earlier.
delete won't
get called if ProcessItem throws an exception, thus creating
garbage. This is a problem in C++ but not in Dylan, which has garbage
collection. We discuss a solution to this problem on
page 266.