6.001 Recitation #6 – Feb 21,
2002
RI: Konrad Tollmar
Types & Higher-order procedures
Programming matters
1. Define a swapping function.
Define a procedure swap that takes a single argument whose type is a function that takes two arguments, and returns a function that acts as the input function but with its argument positions swapped.
(define (swap op)
(lambda (a b) (op b a)))
2. Define a composing function.
A/ Write a procedure composef that takes two arguments (eg. f and g), whose type is a function, and returns a function that first apply g to the input, then f to the result – i.e. ((composef f g) x) should be the same as (f (g x)).
(define (composef
f g)
(lambda (x) (f (g x))))
B/ Use the substitution model to evaluate ((composef double cube) 3).
((composef double cube) 3)
(((lambda (f g) (lambda (x) (f (g x)))) double cube)
3)
;; now expand double and cube:
(((lambda (f g) (lambda (x) (f (g x)))) (lambda (x)
(* x 2)) (lambda (x) (* x x x))) 3)
;; note how confusing it is to have many different
lambdas all with the same parameter
;; name “x” .. we can use the “lambda parameter
renaming trick”, and rename some of the
;; x’s to unused names when we copy in double and
cube:
(((lambda (f g) (lambda (x) (f (g x)))) (lambda (y)
(* y 2)) (lambda (z) (* z z z))) 3)
;; apply the compose lambda to the double and cube
lambdas:
;; here’s the body of compose lambda: (lambda (x) (f
(g x)))
;; f and g are replaced with the double and cube
definitions, so
((lambda (x) ((lambda (y) (* y 2)) ((lambda (z) (* z
z z)) x))) 3 )
;; now apply the composed lambda
((lambda (y) (* y 2)) ((lambda (z) (* z z z)) 3))
((lambda (y) (* y 2)) (* 3 3 3))
((lambda (y) (* y 2)) 27)
(* 27 2)
54
C/ What is the type if composef?
(B->C),(A->B) -> (A->C)
3. Define a function that compose a
function N times.
Rather than:
(define fourth-power (compose square square))
(define eight-power
(compose
square (compose square square)))
Let’s us define a procedure repeated that can compose a function N times, like in:
(define fourth-power (repeated square 2))
(define eight-power (repeated square 3))
(define
(repeated proc n)
(if (= n 0)
(lambda (x) x)
(composef proc (repeated proc (- n 1)))))
Write a new version of repeated that is iterative, i.e. Q(1) in term of space.
(define (repeated proc n)
(define
(iter n ans)
(if
(= n 0)
ans
(iter (- n 1) (compose proc ans))))
(iter n (lambda (x) x)))
4. More higher-order procedures.
Write a function
comp that takes two arguments a and b and returns a function, that when called with #t returns a and when called with #f returns b.
(define comp
(lambda (a b)
(lambda
(x)
(if
x a b)))
)
5. A new list abstraction.
Finding the length of a list structures can be slow!. Define a new sequence abstraction, similar to lists, but that can return the length in constant time.
Building an abstractions:
- Constructor
list->seq
attach
- Accessors
(head seq) -> item
(tail seq) -> seq
- Contract
(head (attach x seq)) == x
(tail (attach x seq)) ==
seq
(seq-empty? empty-seq) ==
#t
(seq-empty? (attach x
seq)) == #f
(seq-length seq) == length
in Q(1) time.
- Layered
Operations
seq->list
- Abstraction
Barrier -----------------------------
- Concrete Representation & Implementation
A/ Define the data abstraction for sequence
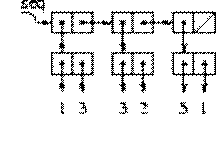
B/ Implement the procedures head, tail and seq-length.
(define seq-empty? null?)
(define head (seq) (car seq))
(define tail (seq) (cdr seq))
(define (seq-length seq) (cdar seq))
C/ The smarter sequence perform better than List, but we need to functions that could convert a Sequence to a List. And vise versa. Define the constructor, list->seq, and the helper-functions, seq->list.
(define (attach seq item)
(cons (cons item (+ 1 (seq-length tail)))
seq)
(define (seq->list seq)
(map car seq))
(define (list->seq lst)
(define (helper lst n)
(if (null? lst)
nil
(cons (cons (car lst) n)
(helper (cdr
lst) (- n 1)))))
(helper lst (length lst)))