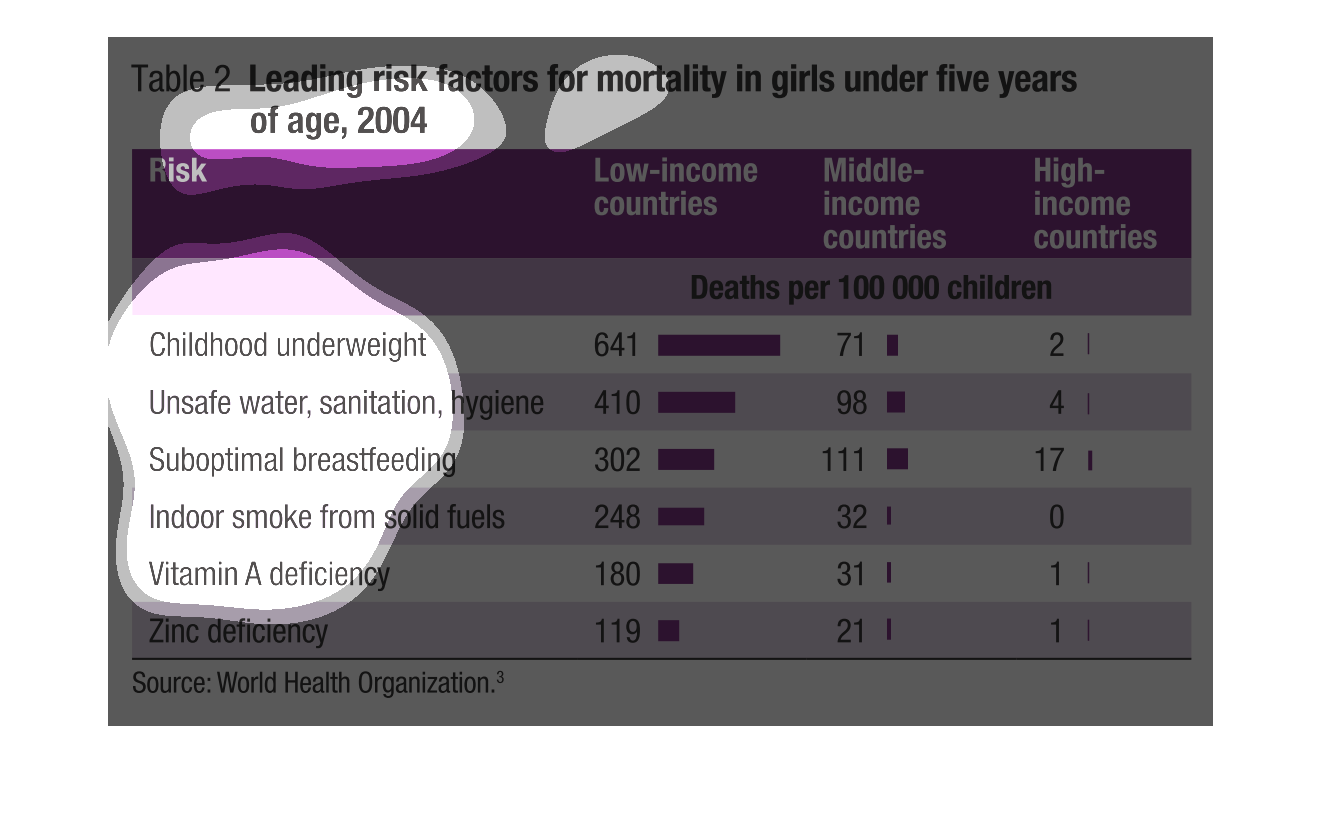
This graph shows leading risk factors for mortality of girls under five years of age in 2004.
It displays risks and factor in high income countries, middle income countries, and low income
countries for factors such as underweight.


The image on the left hand side is a graph helping to understand the leading risks to deaths
of girls under five years of age. From an analysis low income countries have the highest
rate of deaths for girls under five years of age. The leading cause of this death is these
girls being under-weight.

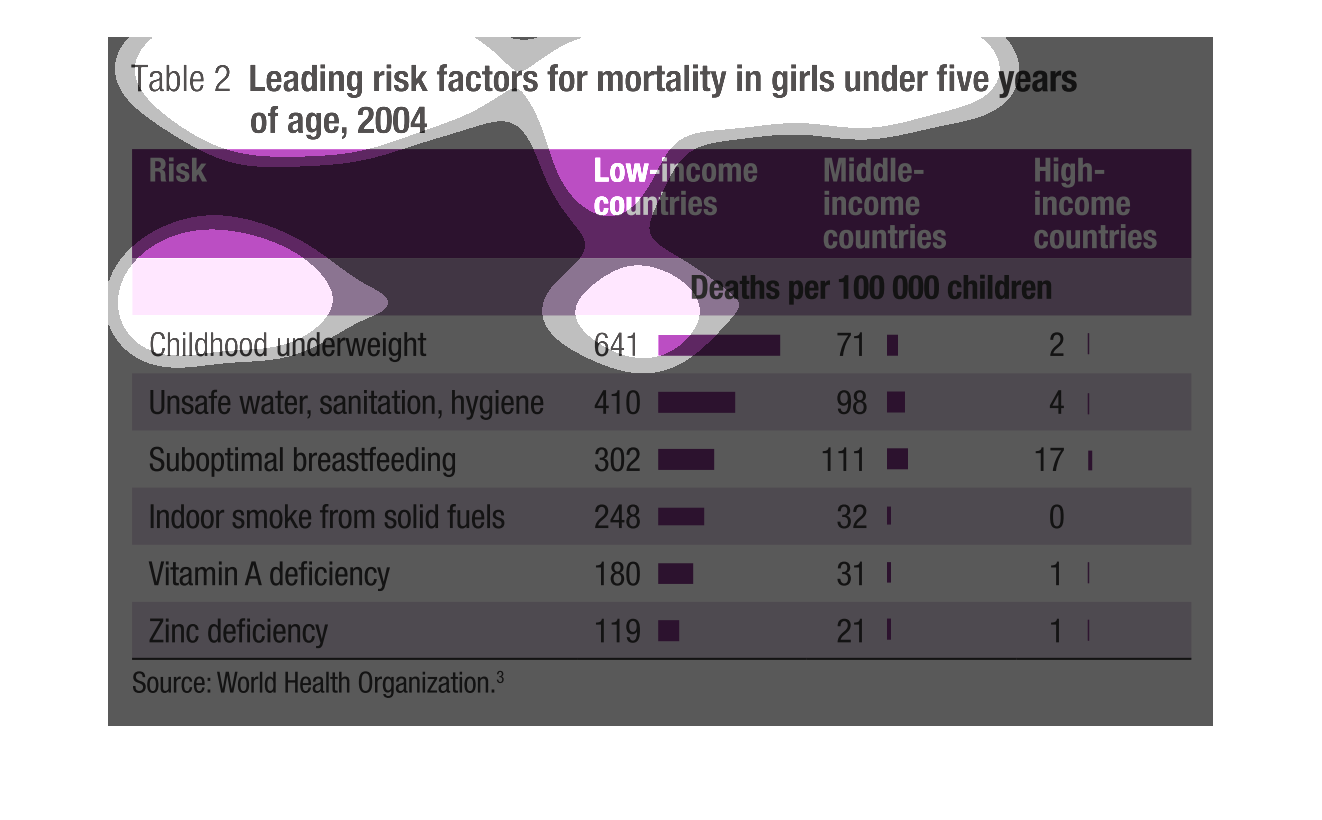
This graph describes leading risk factors for girls under 5 in 2004. Deaths occurred primarily
in low-income countries. Starvation, unclean water, poor breastfeeding habits and fuel smoke
were major killers.


There is a caption for this graph, "Leading risk factors for mortality in girls under five
years of age, 2004". The left hand side of the graph lists six risk factors. To the right
of this are three columns with the headings, "Low income, middle income, and high income countries,
respectively.

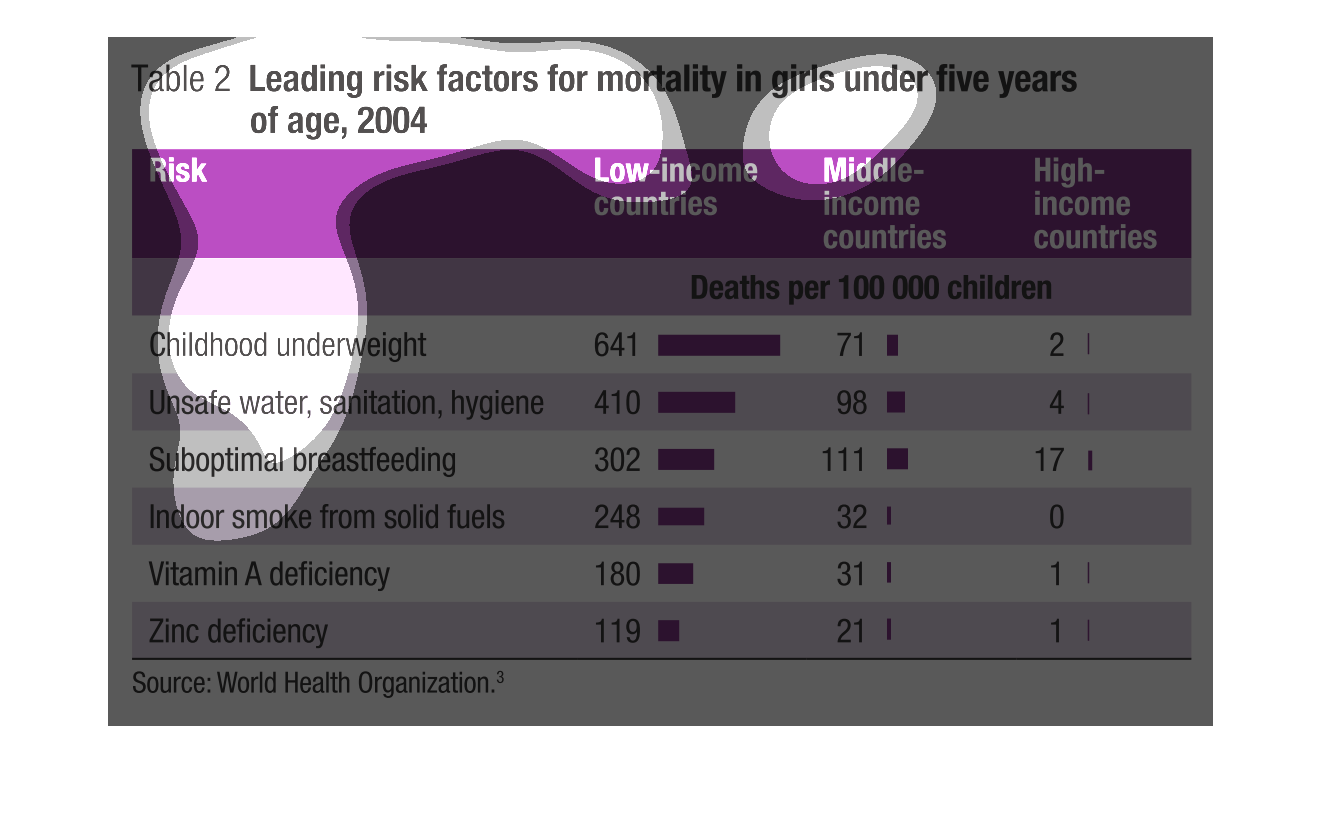
This interesting chart is titled: Leading risk factors for mortality in girls under five years
of age, 2004. On the chart is says risk, Low income countries, middle income countries, and
high income countries.
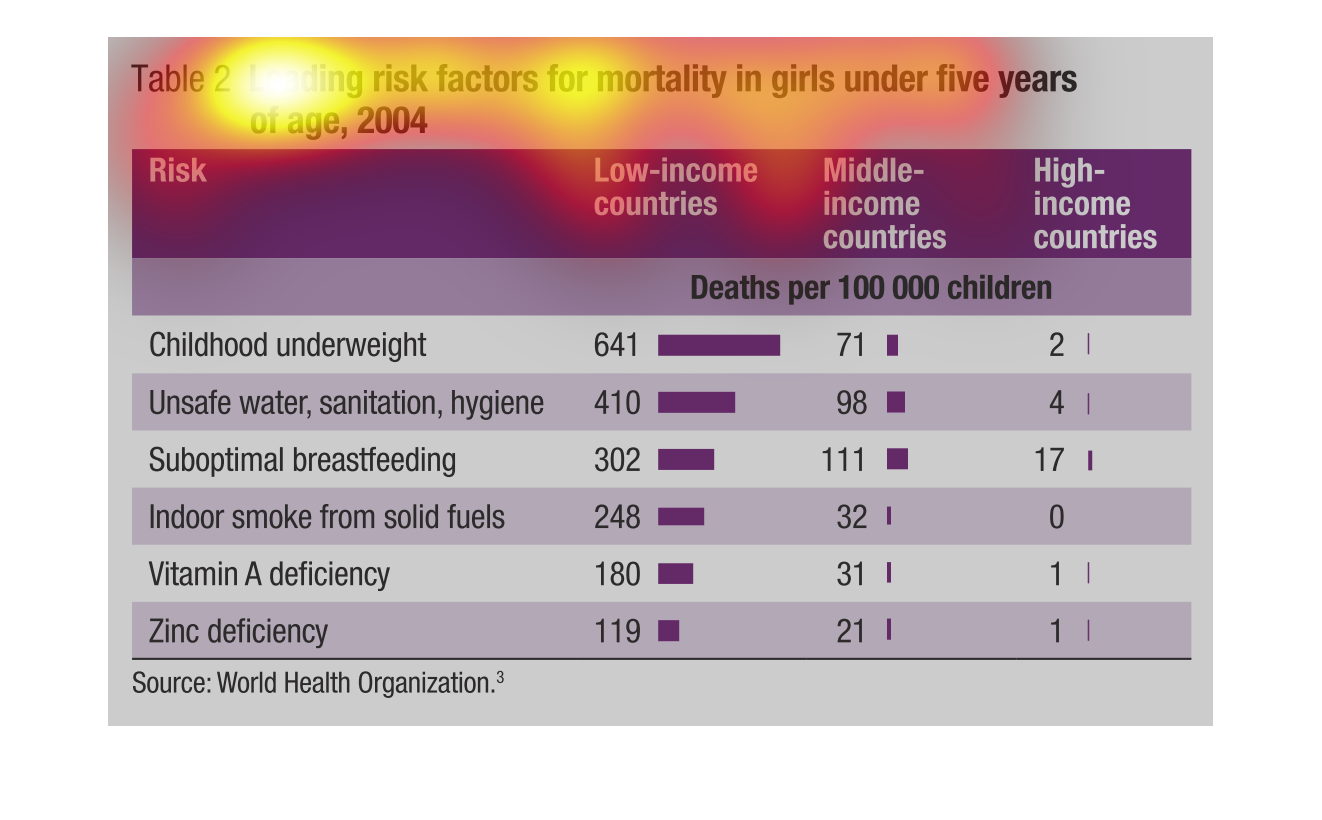

This chart describes leading risk factors for mortality in girls under five years of age for
the year 2004. Categories on the chart include childhood underweight.

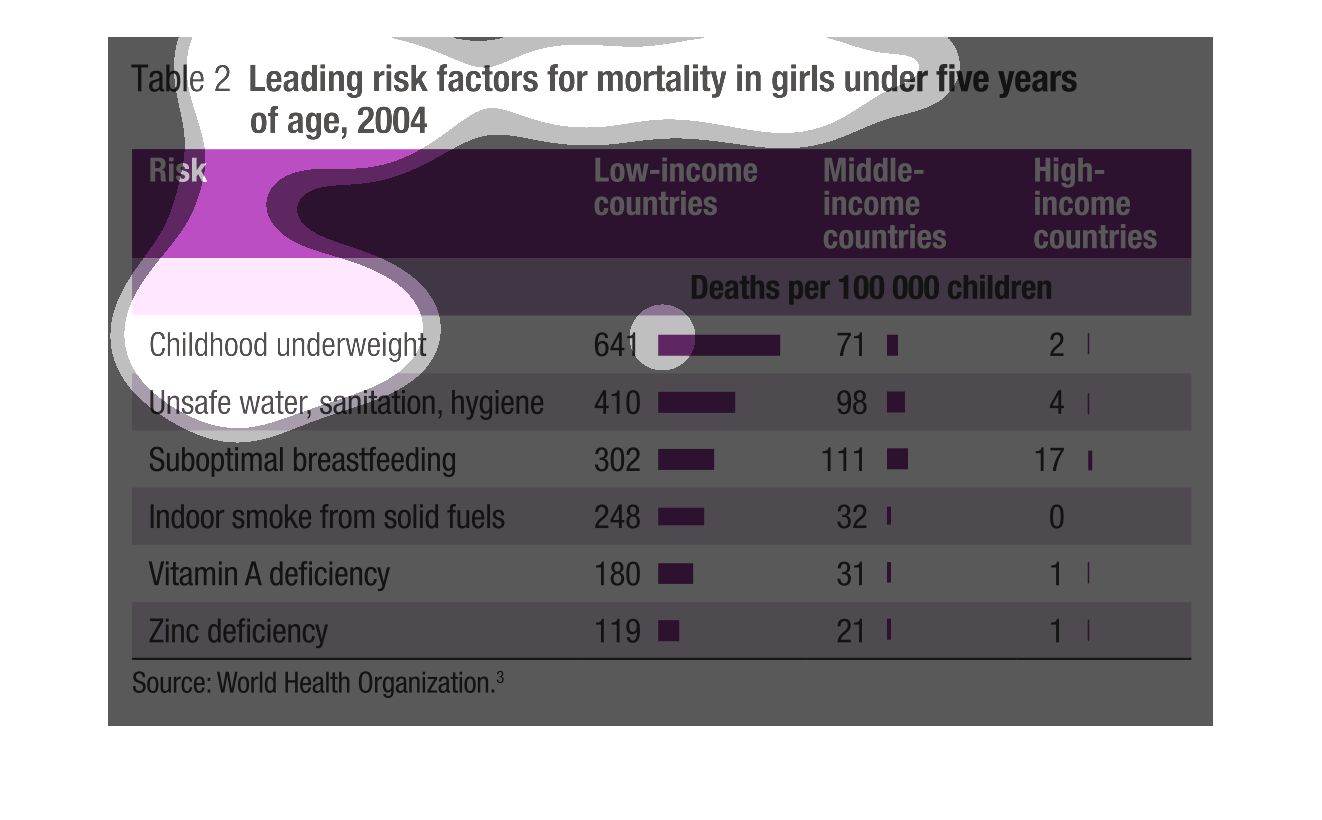
This chart shows the mortality rates in young girls under five years old. In 2004 the study
was conducted and broken down in all the different factors of death.

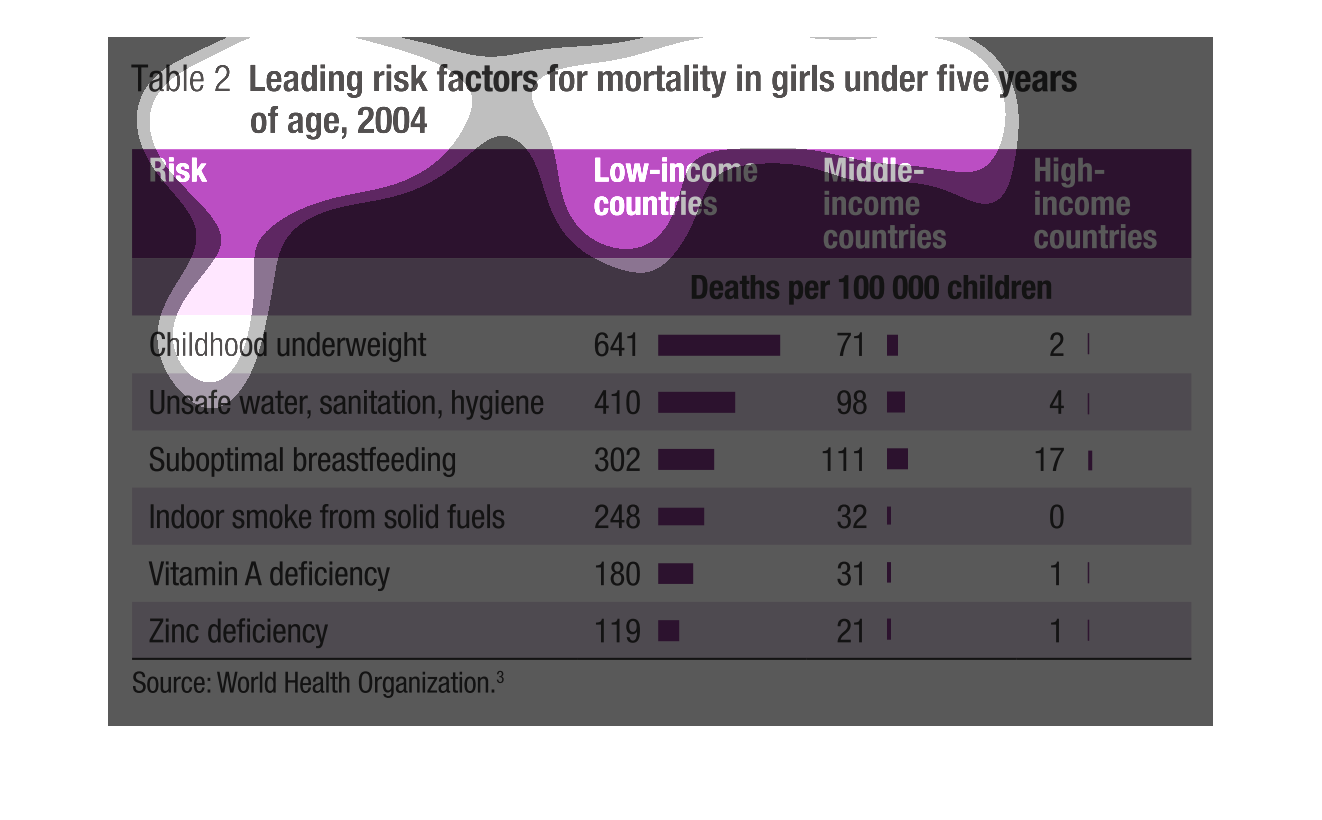
The following chart gives information on mortality on females aged 0-5 years in different
countries. The countries are broken down into low income countries, Middle Income Countries
and high income countries.
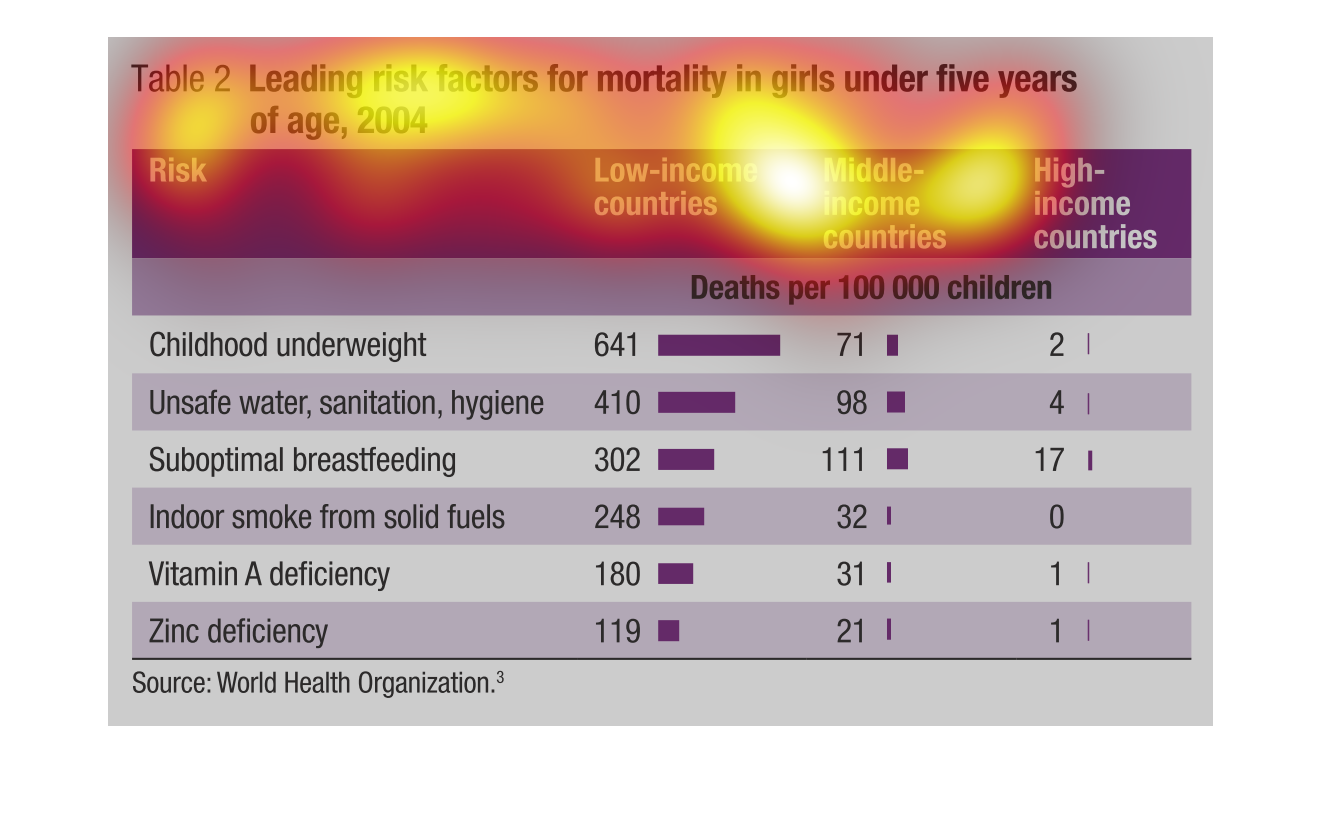
This is a graph showing the leading mortality rate in girls under five years old. The top
reason is the child is underweight at 2. The least of the reasons is a zinc deficiency.


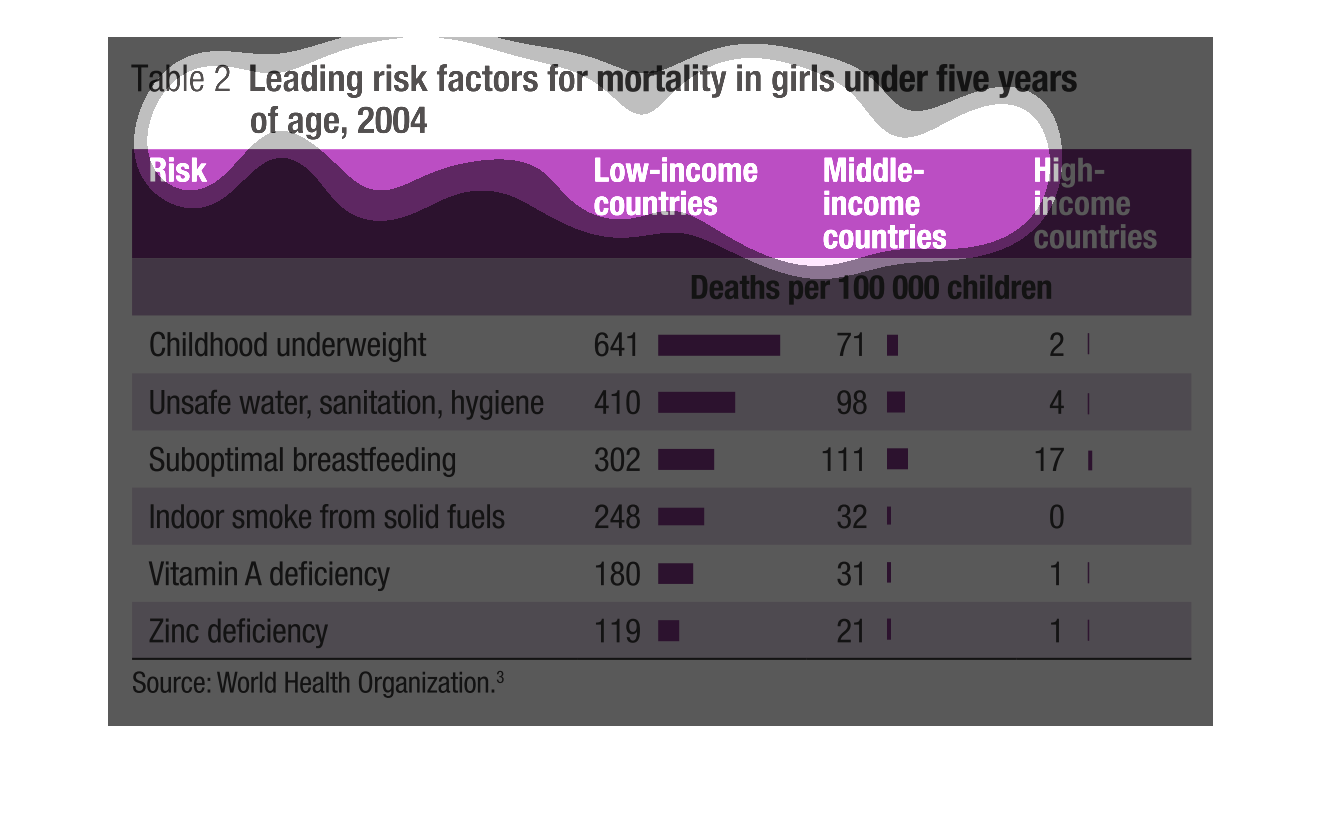
Graph describes about Leading risk factors for mortality in girls under five years of age,
2004. Graph has information about risk in the Low-income countries, Middle-income countries,
High-income countries. Highest risk being childhood underweight with 641 deaths(per 100000
children) and in middle income countries it is 71 deaths and in High-income countries it is
2 deaths. Lowest risk being Zinc deficiency with 119 deaths(per 100000 children) in low-income
countries, 21 deaths in middle-income countries and 1 death in high income countries.


the chart is of leading risks of mortality in girls under the age of 5 the least being zinc
deficancy and the most being childhood underweight it also shows statistics involving the
wealth of the countries from which they are from


This chart is about leading risk factors for mortality in girls under 5 years old. Factors
include childhood underweight, unsafe water, sanitation, sub optimal breastfeeding, indoor
smoke from solid fuels, Vitamin A deficiency, Zinc deficiency. Out of these causes, being
underweight is the leader with 641 out of 100,000 children. Source: World Health Organization.

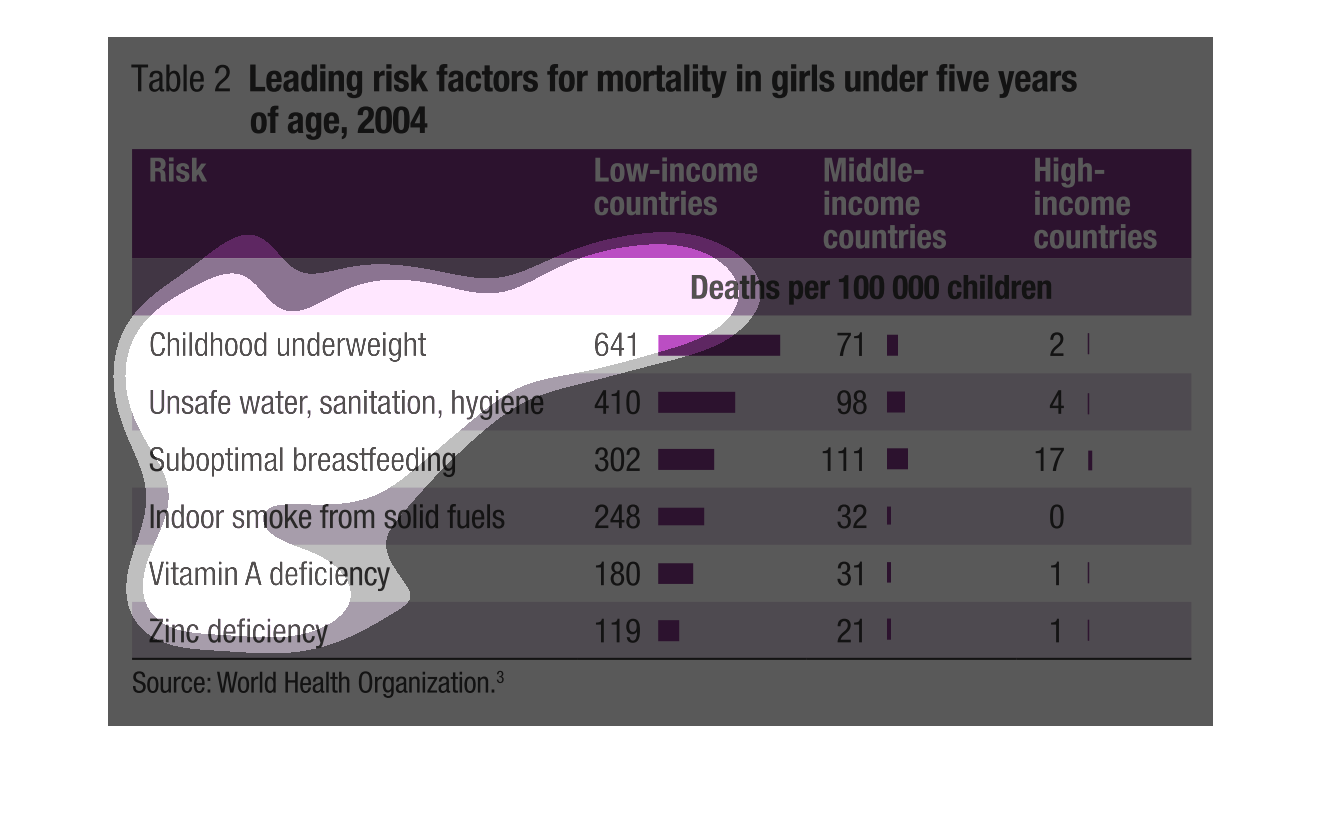
This is a table displaying the information of the leading risk factor for mortality rates
for girls under five years of age in 2004. They compared the stats of Low-income, Middle-income,
and High income countries.


The image depicts the leading causes of mortality in girls under five years of age in the
year 2004. Risk is assessed by category of: Low-income countries, Middle-income countries,
and High-income countries. Leading causes are: Childhood underweight, unsafe water/sanitation/hygiene,
sub-optimal breastfeeding, indoor smoke from solid fuels, vitamin A deficiency. and zinc deficiency.
Source is World Health Organization.

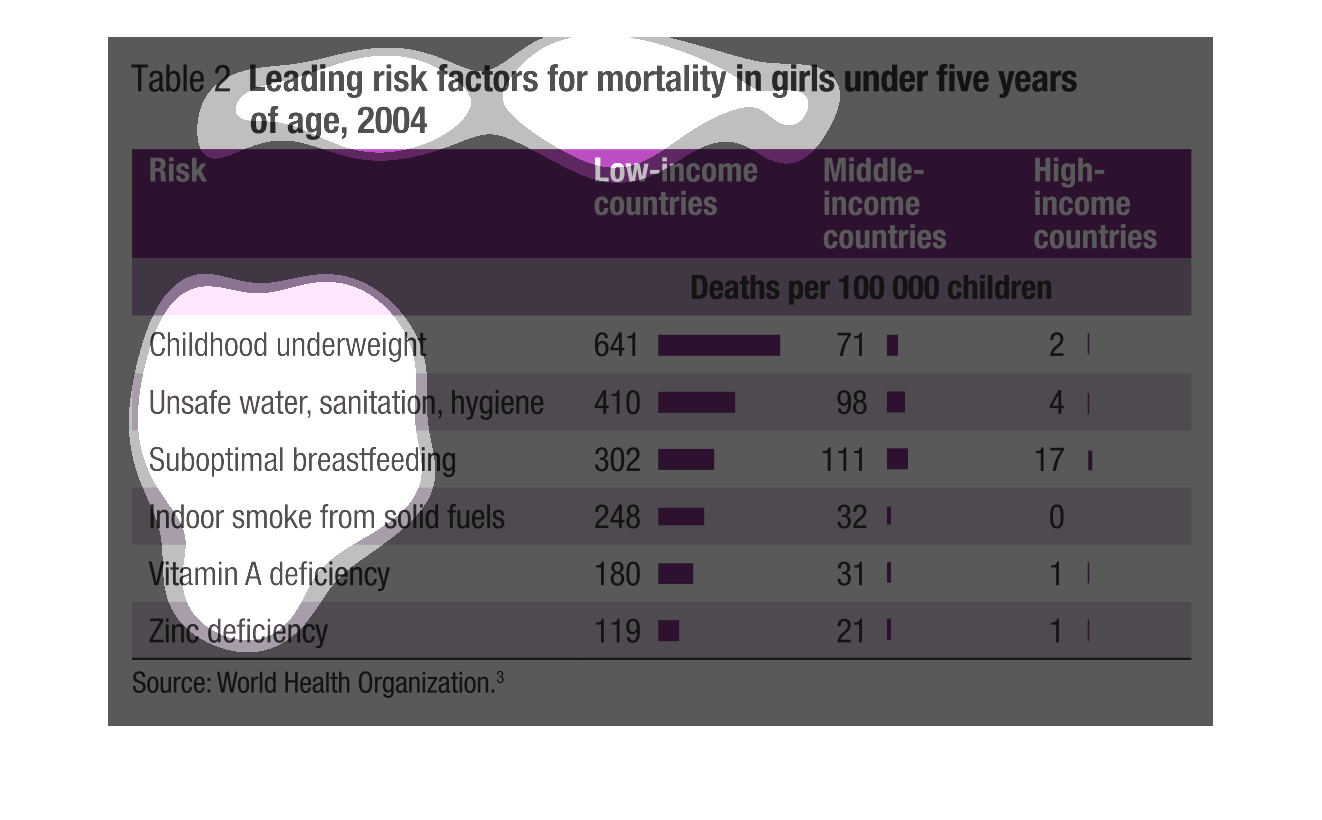
This describes the leading risk factors for mortality in girls under five years of age 2004.
There is a risk category, followed by a low income category, then a middle income and high
income category. For each of the above stated categories are subcategories which include,
childhood underweight, unsafe water sanitation, hygiene, sub-optimal breast feeding, indoor
smoke from solid fuels, vitamin A deficiency, zinc deficiency.