


Next: Assignment Graph, Liveness Condition,
Up: Problem Statement
Previous: Sensing model and control
Since the Dubins car vehicle model has differential constraints which prevent the vehicle from turning arbitrarily fast, when two agents are chasing each other and get very close, they may not be able to keep each other in the windshield anymore. In such cases, they may keep turning to one side to circle each other forever. This phenomenon may also occur in general with 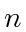 agents chasing one another in a cyclic fashion [28]. To resolve this, we introduce the assumption throughout the paper that once agent
agents chasing one another in a cyclic fashion [28]. To resolve this, we introduce the assumption throughout the paper that once agent 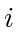 and its target agent
and its target agent 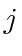 are within a small predetermined distance
are within a small predetermined distance 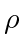 , they combine into a single agent. We call this operation merging and
, they combine into a single agent. We call this operation merging and 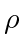 the merging radius. A formal definition will be given in the next section after the concept of assignment graph is defined. If two agents have each other as targets, then merging is mutual, in which case they as a whole are considered as having no target and both stop moving. In practice, merging can be achieved by synchronizing the control for the involved agents.
the merging radius. A formal definition will be given in the next section after the concept of assignment graph is defined. If two agents have each other as targets, then merging is mutual, in which case they as a whole are considered as having no target and both stop moving. In practice, merging can be achieved by synchronizing the control for the involved agents.
With the Dubins car vehicle model, three possible sensing outputs, three control inputs, and the merging assumption, we want to determine conditions under which agents are guaranteed to rendezvous, involving no state estimation using coordinates.



Next: Assignment Graph, Liveness Condition,
Up: Problem Statement
Previous: Sensing model and control
Jingjin Yu
2011-01-18