-
Guided Filter is included in Wikipedia
 as a representative edge-preserving smoothing technique.
as a representative edge-preserving smoothing technique. -
Guided Filter is included in official MATLAB 2014
 as a new function.
as a new function. -
Guided Filter is included in official OpenCV 3.0
 as a new function.
as a new function.
Guided Image Filtering
| Kaiming He |
| Microsoft Research |
|
|
|
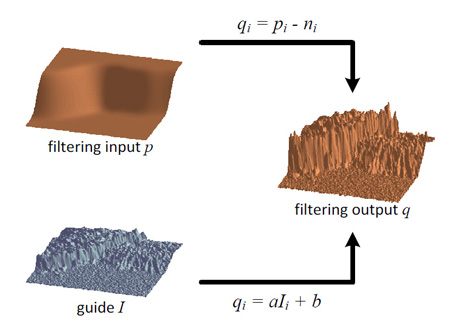
Abstract In this paper we propose a novel explicit image filter called guided filter. Derived from a local linear model, the guided filter computes the filtering output by considering the content of a guidance image, which can be the input image itself or another different image. The guided filter can be used as an edge-preserving smoothing operator like the popular bilateral filter, but has better behaviors near edges. The guided filter is also a more generic concept beyond smoothing: it can transfer the structures of the guidance image to the filtering output, enabling new filtering applications like dehazing and guided feathering. Moreover, the guided filter naturally has a fast and non-approximate linear time algorithm, regardless of the kernel size and the intensity range. Currently it is one of the fastest edge-preserving filters. Experiments show that the guided filter is both effective and efficient in a great variety of computer vision and computer graphics applications including edge-aware smoothing, detail enhancement, HDR compression, image matting/feathering, dehazing, joint upsampling, etc.
Try the guided filter in any situation when the bilateral filter works well. The guided filter is much faster and sometimes (though not always) works better. |
|
Related Publications:
See Also:
Resources: |