Machine Learning from Human Experts
Coordinating humans and robots to complete a set of jobs with temporal and resource constraints is computationally challenging, yet human domain experts can solve these difficult scheduling problems using paradigms learned through years of apprenticeship. To autonomously learn from domain experts how to solve these complex planning and scheduling problems, I propose a new machine learning technique, which I call "Apprenticeship Scheduling."
see more...
FURTHER READING
Matthew C. Gombolay, Xi Jessie Yang, Brad Hayes, Nicole Seo, Zixi Liu, Samir Wadhwania, Tania Yu, Neel Shah, Toni Golen, and Julie A. Shah. Robotic Assistance in Coordination of Patient Care. In Proc. Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2016. Cite. [24% Acceptance Rate]
Matthew C. Gombolay, Jessica Stigile, Reed Jensen, Sung-Hyun Son, and Julie A. Shah. Apprenticeship Scheduling: Learning to Schedule from Human Experts. In Proc. International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2016. Cite. [25% Acceptance Rate]
DYNAMIC SCHEDULING OF HUMAN-ROBOT TEAMS
New uses of robotics in traditionally manual manufacturing processes require the careful choreography of human and robotic agents to support safe and efficient coordinated work. Tasks must be allocated among agents and scheduled to meet temporal deadlines and spatial restrictions on agent proximity. These systems must also be capable of replanning on-the-fly to adapt to disturbances in the schedule and to respond to people working in close physical proximity.
see more...
FURTHER READING
Matthew C. Gombolay, Ron J. Wilcox, and Julie A. Shah. Fast Scheduling of Multi-Robot Teams with Temporospatial Constraints. In Proc. Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS) 2013. [30% Acceptance Rate]
HUMAN-ROBOT INTERACTION
I believe that it is essential we take a human-centered approach when integrating automation or robots into the workplace. A core component of my research is conducting multifaceted, human-subject experiments to understand the impact of integrating robots into human-robot teams for a human factors perspective.
see more...
FURTHER READING
Matthew C. Gombolay, Reymundo A. Gutierrez, Shanelle G. Clarke, Giancarlo F. Sturla, and Julie A. Shah. Decision-Making Authority, Team Efficiency, and Human Worker Satisfaction in Mixed Human-Robot Teams. Autonomous Robots, vol. 39, issue 3, pp. 293-312, 2015. Cite.
Matthew C. Gombolay, Reymundo A. Gutierrez, Giancarlo F. Sturla, and Julie A. Shah. Decision-Making Authority, Team Efficiency, and Human Worker Satisfaction in Mixed Human-Robot Teams. In Proc. Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS) 2014. [32% Acceptance Rate]
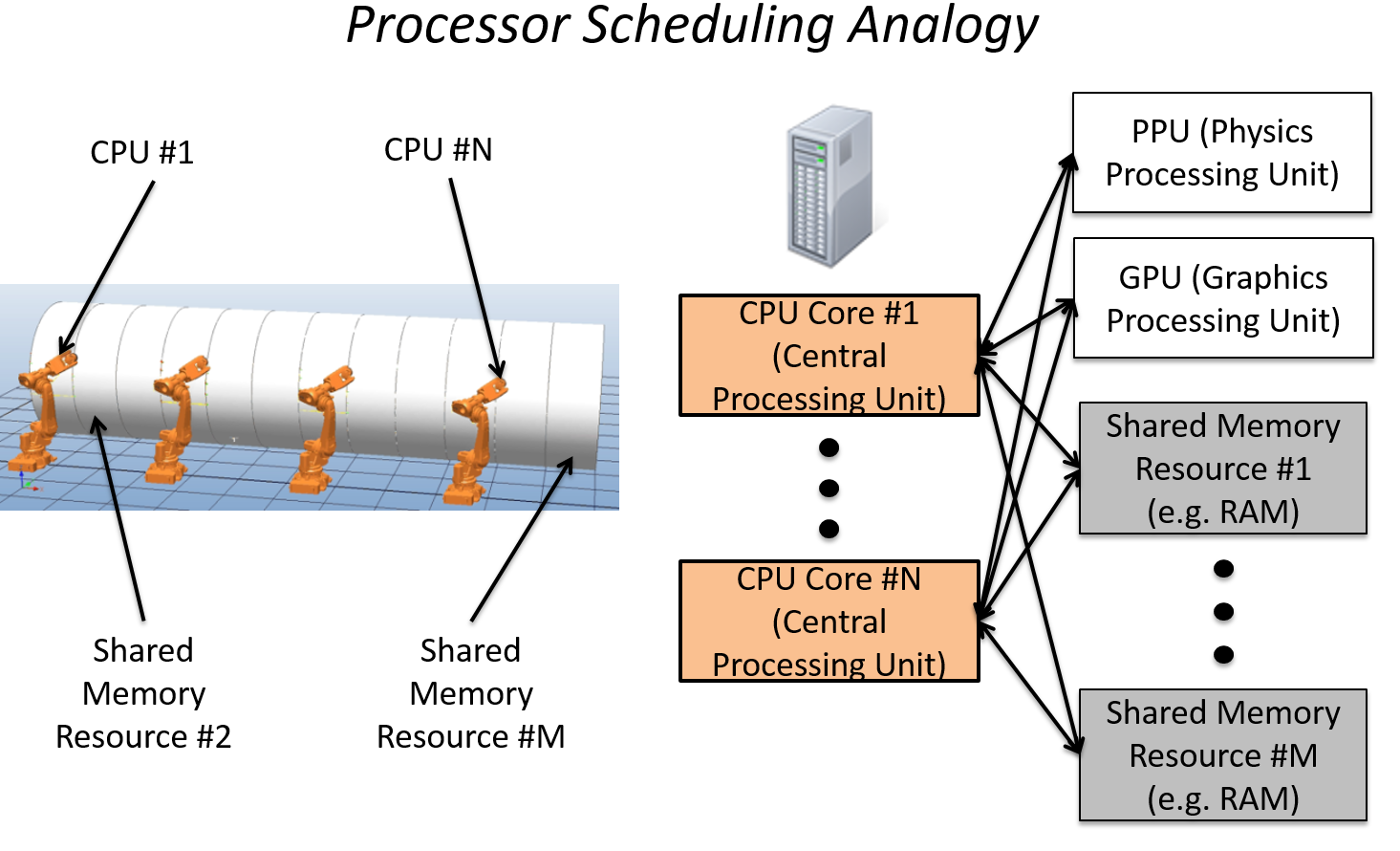
REAL-TIME PROCESSOR SCHEDULING
Traditional scheduling in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Operations Research (OR) often rely on methods for scheduling that are too slow for real-time, dynamic scheduling of large task sets. While real-time processor scheduling techniques are fast, they are often uninformative for more general, real-world problems. One goal of my research is to bridge the gap of these communities to provide methods for scheduling that are fast enough for real-time systems yet provide near-optimal solutions for real-world problems.
see more...
FURTHER READING
Matthew C. Gombolay, Ron J. Wilcox, and Julie A. Shah. Uniprocessor Scheduling Policy for Non-Preemptive Task Sets with Precedence and Temporal Constraints. In Proc. AIAA Infotech@Aerospace 2012. *AIAA BEST INTELLGIENT SYSTEMS PAPER AWARD 2012