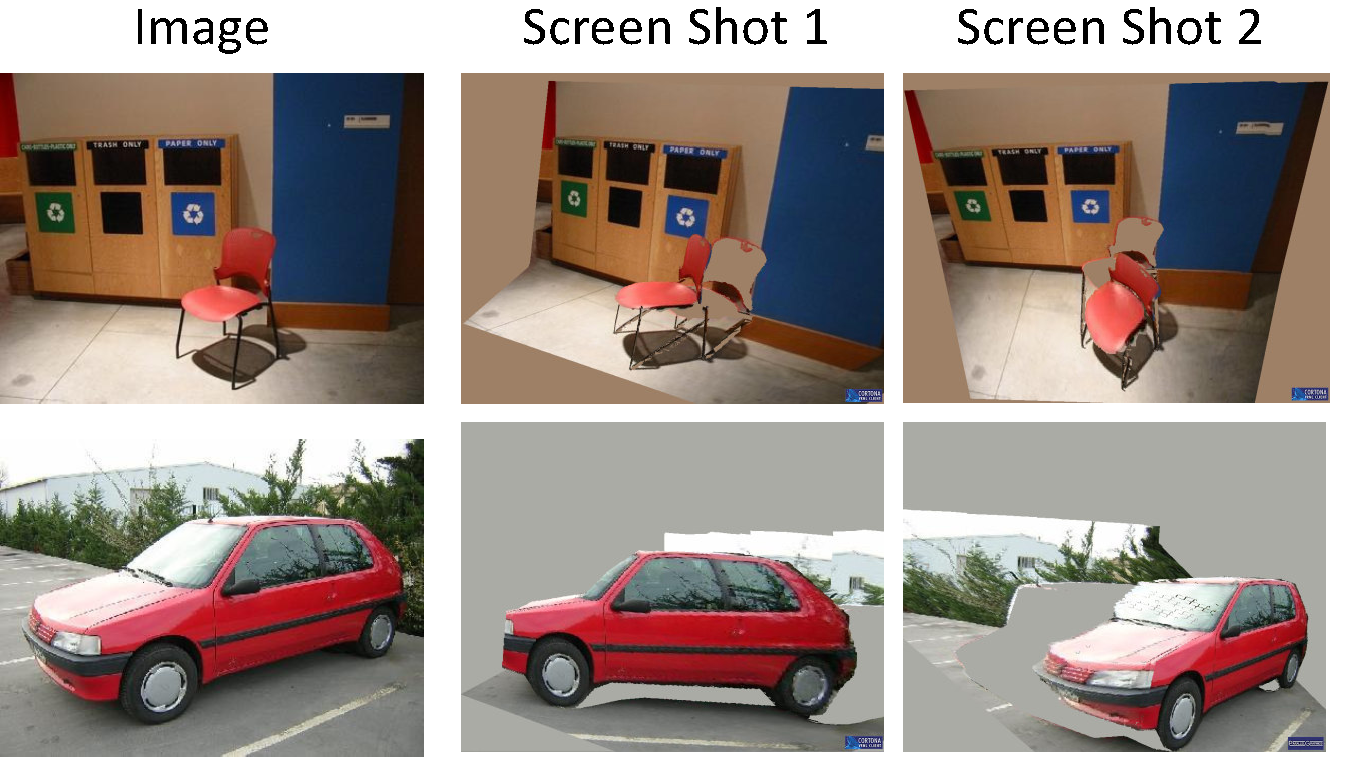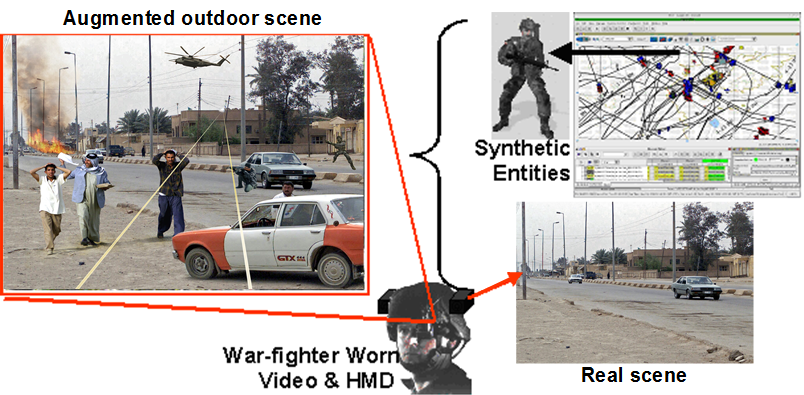
ASPN (All Source Positioning and Navigation)
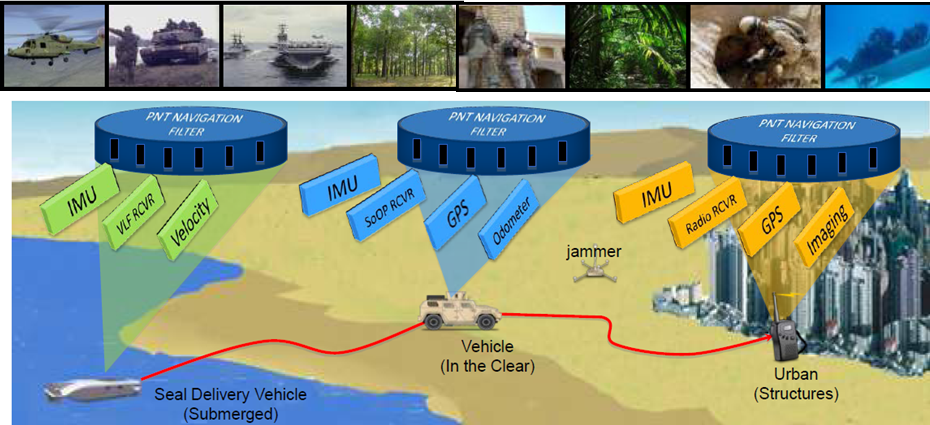
This project seeks to enable low cost, robust, and seamless navigation solutions for users on any operational platform and in any environment. We collaborate with academic researchers at Georgia Institute of Technology and MIT, and government agencies. We are currently developing real-time navigation algorithms and systems needed for rapid integration and reconfiguration of any combination of sensors, by using approaches based on Factor Graphs. In our framework, each sensor measurement is encoded as a factor. This way provides an adaptable and flexible foundation for any plug-and-play sensor. So far we have tested our system with 19 different sensor types (total 57 sensors: each sensor type includes multiple kinds of sensors) mounted on dismount, ground, and aerial platforms...
[more]