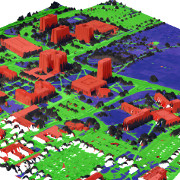
CVPR 2019: StereoDRNet: Dilated Residual Stereo Net
We propose a system that uses a convolution neural network (CNN) to estimate depth from a stereo pair followed by volumetric fusion of the predicted depth maps to produce a 3D reconstruction of a scene. Our proposed depth refinement architecture, predicts view-consistent disparity and occlusion maps that helps the fusion system to produce geometrically consistent reconstructions. We utilize 3D dilated convolutions in our proposed cost filtering network that yields better filtering while almos...